How Intelligent Packaging Is Helping Address the Problem of Plastic Globally

How Intelligent Packaging Is Helping Address the Problem of Plastic Globally
Plastic is present in every conceivable place, including our bodies, our seas, and even our kitchens. Due to the fact that it is long-lasting, inexpensive, and convenient, it has been the material of choice for packaging for many decades. However, the cost to the ecosystem has been very detrimental. There are hundreds of millions of tons of trash plastic produced throughout the globe each year, the majority of which is disposed of in a manner that pollutes natural ecosystems and causes damage to species. Even while recycling initiatives have been useful, they have not been sufficient.
At this time, when the globe is facing an increasing dilemma with climate change and waste, a new strategy that is gaining popularity is smart packaging. This is not just about reducing the amount of plastic that we use; rather, it is about entirely rethinking how we design, use, and dispose of materials that are used for packaging. In order to build a future in which the things that we throw away do not have a negative impact on the environment, smart packaging combines elements of creativity, sustainability, and even digital technology.
Let us investigate the ways in which intelligent packaging is assisting us in addressing one of the most significant environmental concerns of our day.
What Is the Issue with Packaging Made of Plastic?
It’s not simply trash that’s contributing to the worldwide plastic crisis. A system that was designed for convenience rather than for long-term sustainability is at issue here. Packaging made of plastic, particularly plastic that is intended for a single use, is intended to be discarded. The reality, however, is that plastic does not disappear. In addition to contaminating water sources and often making its way into the food chain, it causes the breakdown of microplastics.
Unfortunately, only a tiny fraction of plastic is really recycled. This is a very unfortunate situation. A significant portion of it is disposed of in landfills or incinerators, and an astounding quantity is discharged into rivers and seas on an annual basis. The traditional recycling processes are restricted in many locations due to cost constraints, pollution, and a lack of sufficient infrastructure. Despite the fact that we have known this for years, the situation has simply gotten worse.
This is why there is optimism in the use of smart packaging. Not just in terms of replacing plastic, but also in terms of developing whole new systems for the packaging of commodities that will cut down on waste, increase shelf life, and promote circular economies.
How exactly does one define “smart packaging”?
The term “smart packaging” refers to packaging that has been cleverly created, either in terms of the materials it is made of, the purpose it serves, or the technology it employs. There is a great deal more to it than just being recyclable or biodegradable. The use of integrated sensors or QR codes allows for smart packaging to connect with customers, monitor the freshness of the product, minimize the amount of food that is wasted, and prolong the product’s shelf life.
Active packaging and intelligent packaging are the two primary categories that fall under the umbrella term “smart packaging.” To maintain the product’s freshness, active packaging engages in a variety of interactions with the product, such as absorbing oxygen or managing moisture levels. As an example, freshness indicators, temperature records, and authentication features are all examples of the types of data that may be gathered or sent by intelligent packaging.
Most notably, a significant number of these advances are centered on the elimination of dependency on plastic entirely via the use of materials that are either renewable, biodegradable, or reusable.
Solutions for Packaging Made from Plants and Compostable Materials
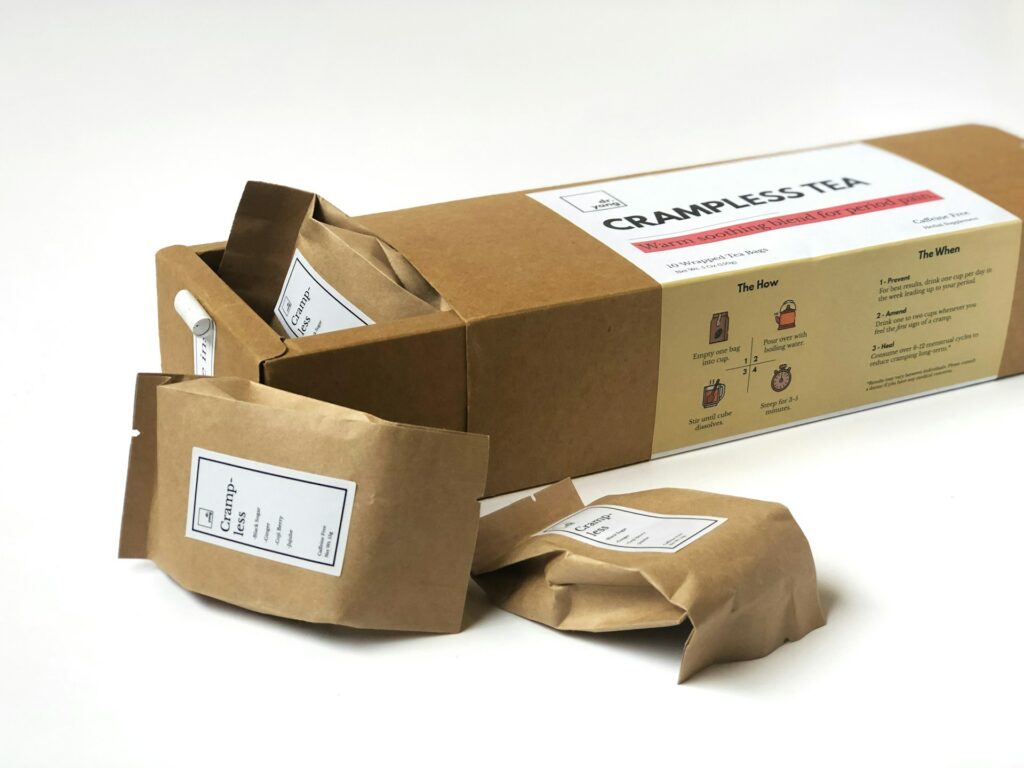
Plant-based materials that imitate plastic but decompose organically in the environment are becoming more popular, which is one of the most exciting advances in the field of smart packaging now taking place. For example, products manufactured from maize starch, sugarcane, seaweed, and even mushrooms are included in this category.
Currently, businesses are manufacturing packaging that may be composted either at home or at industrial facilities. This kind of packaging is returned to the soil rather than contributing to the pollution of the environment. Some new businesses are experimenting with edible packaging, while others are transforming waste from agricultural production into fiber-based boxes and films. One of the most obvious benefits is that these materials disintegrate in a matter of weeks or months, rather than millennia, and they do not release any harmful chemicals into the soil or water. In addition, many of them are renewable, which means that they may be created again without diminishing the resources that are available.
The packaging of a product that indicates when it should be used (or thrown away)
One of the most significant sources of waste in the packaging industry is items that have gone bad or have expired, particularly in the food and medical sectors. But what if the package itself has the ability to be a preventative measure?
A solution to this problem is the use of clever packaging. In the event that a food item has lost its freshness, some new materials may undergo a color shift. Among the others are temperature sensors that provide shippers and customers with information on whether or not an item was kept incorrectly. These intelligent indicators contribute to the reduction of waste by ensuring that items are used at the appropriate time and are not discarded before their time has come.
Time-temperature indicators, for instance, are now being tested on some milk cartons. These indications determine whether or not the food has been kept cool during the transportation process. In the event that this is not the case, the package will visibly warn you. In addition to ensuring the safety of customers, this kind of data-driven packaging also contributes to the reduction of the tremendous environmental cost that is associated with food rotting.
In what ways does technology and digital packaging play a role?
Packaging is becoming an integral aspect of the digital experience given the prevalence of e-commerce and data in today’s world. Some firms are incorporating QR codes and NFC chips into their packaging in order to disseminate information like the origin of their products, instructions for recycling, or verification of their legitimacy. This is particularly helpful for firms that are attempting to earn the confidence of customers who are environmentally sensitive.
Reusable systems, in which packaging is monitored, returned, and refilled rather than wasted, are another use for digital packaging, which plays a part in these systems. In some locations, trial programs are now being implemented in which customers may place orders for groceries or takeout in containers that can be reused and then bring them to pickup sites. Artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology are even being utilized to verify the effectiveness and openness of these systems.
Packaging, and the systems that handle it, are becoming more intelligent. In a nutshell, this is the case.
- Continued Obstacles to Overcome
However, despite the fact that it is a game-changer, smart packaging is not without its obstacles. It is common for biodegradable materials to need certain composting conditions in order to decompose in the appropriate manner. It is still difficult to find infrastructure that allows for the composting or recycling of smart materials in many regions of the globe. Also, the cost of innovative materials and technologies is often higher than the cost of conventional plastic.
In addition, there is a lack of clarity among customers on what constitutes genuine sustainability. It is not always the case that anything will decompose in your lawn just because it has a green appearance or the word “compostable” on it. Labeling that is easy to understand and education of the general public are both necessary components for the success of smart packaging on a worldwide basis.
In order to facilitate this shift, governments and companies need to collaborate in order to provide the appropriate incentives, legislation, and technological infrastructure.