The Part Played by Virtual Reality in Immersive News Experiences
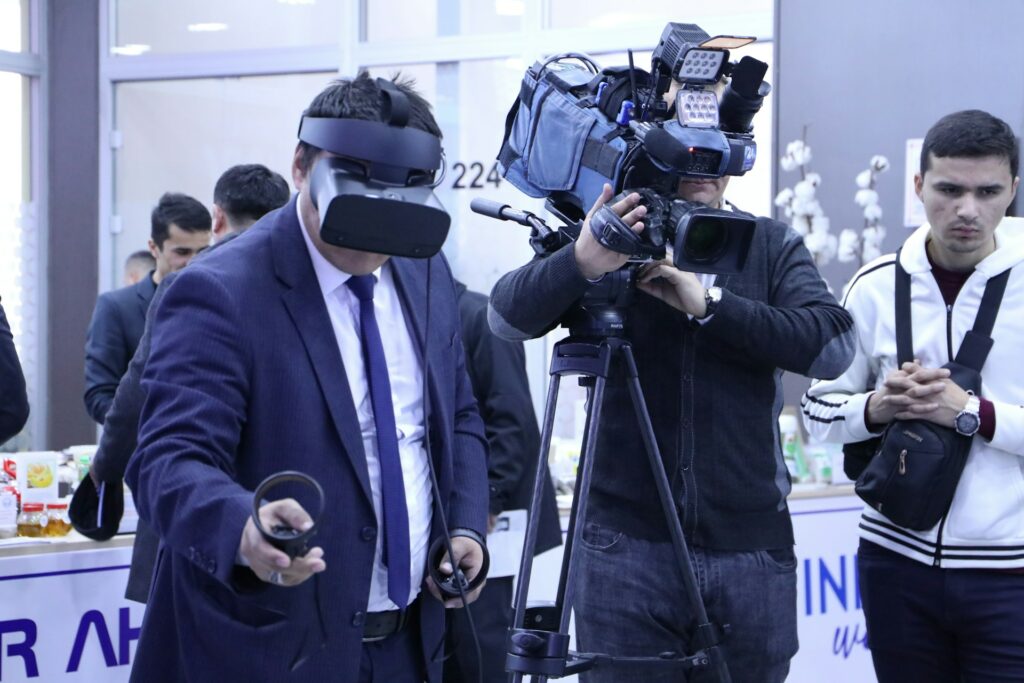

The Part Played by Virtual Reality in Immersive News Experiences
For generations, the field of journalism has depended on words, images, and, finally, video to bring global events closer to viewers. Nevertheless, the most captivating forms frequently fail to properly express the weight or depth of a tale, despite their best efforts. Virtual Reality (VR), which is a technology that has the ability to transfer viewers to the center of a news event, so enabling them to observe and even engage with stories as if they were physically there, is now available. Virtual reality has the potential to alter the way that news is consumed by audiences, converting them from passive readers into active participants in immersive experiences.
1. Defining VR in Journalism
The use of immersive, computer-generated environments that duplicate real-world situations or recreate events is what is meant when virtual reality is discussed in the context of journalism. Virtual reality (VR) technology enables viewers to immerse themselves in a narrative from a first-person viewpoint, navigating around an area, noticing details, and interacting with information in a way that is not possible with conventional news formats.
2. How News Stories Have Changed Over Time
Over time, the formats used to provide the news have changed in parallel with technological advances. For example, newspapers provided reporting that was text-heavy, radio included voices, television supplied moving pictures, and digital platforms contributed interaction. Virtual reality is the next big step in storytelling; it transforms tales into places that can be experienced rather than merely digested.
3. Immersion and Emotional Impact
Empathy building is one of the most potent capabilities that virtual reality (VR) offers. Virtual reality (VR) promotes a more profound knowledge and more meaningful emotional connections by immersing audiences in the center of a refugee camp, a region affected by a climatic calamity, or a political demonstration. The immersive viewpoint has the ability to encourage more social participation by making problems seem less abstract and more personal.
4. Events Reconstructed in 360 Degrees
Events are often recreated in virtual reality (VR) journalism via the use of 360-degree footage or computer-generated reconstructions. This can include visiting a city that has been decimated by war, examining the aftermath of a natural catastrophe, or taking a tour of a historical landmark as part of a feature piece. These kinds of reconstructions make it possible for viewers to experience experiences with more depth and context.
5. Making Complex Reporting Better
There are certain issues that are difficult to effectively communicate using text alone. Examples of these include the topic of climate change, economic injustice, and technological advances. Virtual reality makes it possible for data to be visualized in three-dimensional spaces, where audiences may walk around charts, simulations, or timelines, which makes it simpler for people to understand complicated topics and find the experience more engaging.
6. Audience Participation and Agency
Virtual reality (VR) has the potential to provide users with agency inside a tale, which is something that conventional formats cannot provide. For instance, in a virtual reality news experience, a user would be able to choose the location of their gaze during an interview, follow a simulation through a variety of stories, or investigate an investigative report from a number of distinct points of view. The dynamic function that reporters play in journalism alters the interaction between them and their audience.
7. Difficulties in Achieving Accessibility
Virtual reality (VR) news confronts a number of obstacles in spite of its potential:
- Headsets are still costly and are not yet extensively used, which represents a hardware barrier.
- Costs of production: The production of virtual reality content needs the use of cutting-edge technology and a large amount of resources.
- Restricted reach: Virtual reality devices are not the primary means by which a large number of people get news; they continue to rely on smartphones and computers.
8. Ethical Considerations
Responsibility is an unavoidable consequence of full involvement. When it comes to journalism, what is the best way to communicate delicate subjects such as violence or tragedy in virtual reality without causing viewers to become overwhelmed or traumatized? When it comes to immersive storytelling, making sure that the information is accurate and that the tale is not sensationalized is a significant ethical consideration.
9. The Part Played by Organizations That Report News
Virtual reality (VR) reporting has already been tried out by a few of the most prominent news sources. These experiments have resulted in the creation of documentaries and features that give people the opportunity to experience events in a more personal way. Virtual reality (VR) might potentially be embraced by newsrooms of medium size and those that are situated in small communities as technology becomes ever more accessible in terms of cost. This would provide fresh approaches to interacting with readers.
10. The Future of News That Is Immersive
The immersive news experience is likely to transition from a niche experiment to a normal service as virtual reality (VR) gear becomes more commonplace, more affordable, and lower in weight. It is possible that newsrooms would provide virtual reality briefings on a regular basis in the future, which would give individuals the opportunity to experience a live press conference, visit a crime scene, or investigate events happening across the world without ever having to leave the comfort of their own homes.
By making stories something that people can feel rather than just read or watch, virtual reality is altering the frontiers of journalism. There is no other method of presenting the news that is as effective as immersive reporting when it comes to cultivating empathy, simplifying complicated matters, and increasing the level of audience participation. The potential for virtual reality to transform the way stories are told is apparent, even if there are still issues around accessibility and ethics. As technology continues to develop, it is possible that the distinction between following the news and experiencing it will become less clear, which might lead to a new age of immersive media.